In this short tutorial we will convert MySQL Table into Python Dictionary and Pandas DataFrame. If you need the reverse operation - convert Python dictionary to SQL insert then you can check:
In this tutorial we will use several Python libraries like:
- PyMySQL + SQLAlchemy - the shortest and easiest way to convert MySQL table to Python dict
- mysql.connector
- pyodbc in order to connect to MySQL database, read table and convert it to DataFrame or Python dict.
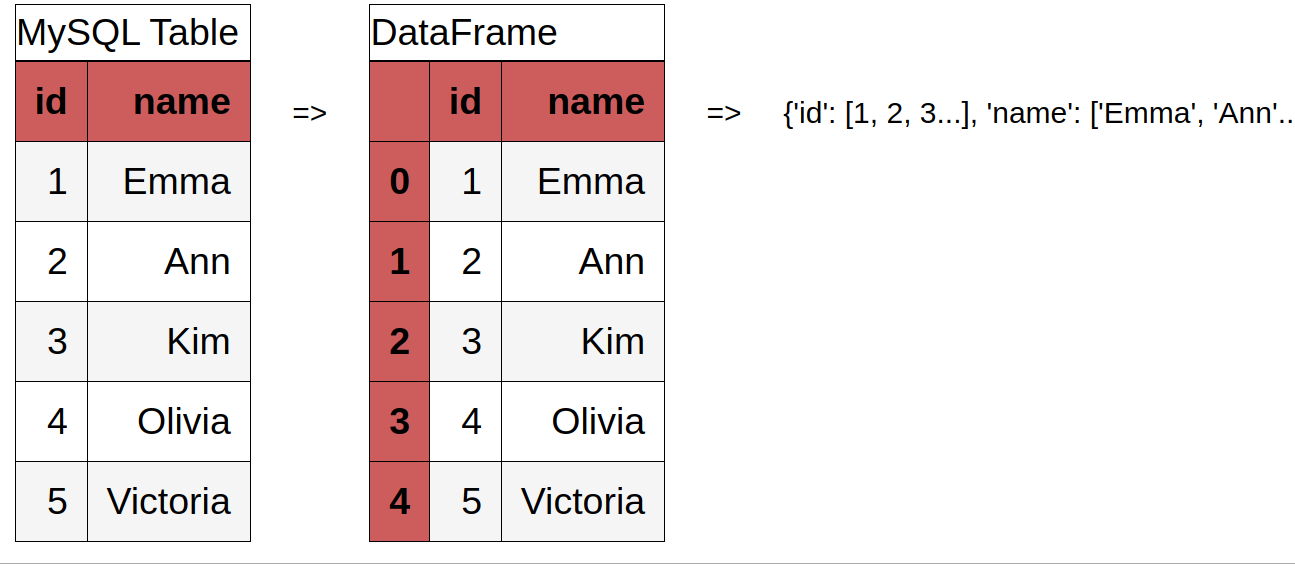
1. Python convert MySQL table to Pandas DataFrame (to Python Dictionary) with SQLAlchemy
1.1. Install libraries SQLAlchemy + PyMySQL
Let's install dependencies required for Python in order to connect to MySQL database - in this case - PyMySQL + SQLAlchemy:
pip install PyMySQL
pip install SQLAlchemy
1.2 Connect to MySQL database
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pymysql
db_connection_str = 'mysql+pymysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/test'
db_connection = create_engine(db_connection_str)
Now we are going to connect to localhost:3306, database is test and the user/password are: root/pass.
1.3 Convert SQL table to DataFrame with SQLAlchemy
df = pd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM girls', con=db_connection)
1.4. Convert SQL DataFrame to dictionary
The final step is to convert a DataFrame to Python dictionary by:
dict1 = df.to_dict('records')
dict2 = df.to_dict('list')
where:
- ‘records’ : list like [{column -> value}, … , {column -> value}]
- ‘list’ : dict like {column -> [values]}
- ‘dict’ (default) : dict like {column -> {index -> value}}
- ‘records’ : list like [{column -> value}, … , {column -> value}]
For more info: pandas.DataFrame.to_dict
1.5. Full Code: MySQL table to Python dict
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pymysql
db_connection_str = 'mysql+pymysql://root:kostov@localhost:3306/test'
db_connection = create_engine(db_connection_str)
df = pd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM girls', con=db_connection)
df.to_dict('list')
result:
{'id': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 'name': ['Emma', 'Ann', 'Kim', 'Olivia', 'Victoria']}
1.6. Control dictionary output
df.to_dict()
[{'id': 1, 'name': 'Emma'},
{'id': 2, 'name': 'Ann'},
{'id': 3, 'name': 'Kim'},
{'id': 4, 'name': 'Olivia'},
{'id': 5, 'name': 'Victoria'}]
df.to_dict('list')
{'id': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 'name': ['Emma', 'Ann', 'Kim', 'Olivia', 'Victoria']}
df.to_dict('records')
[{'id': 1, 'name': 'Emma'},
{'id': 2, 'name': 'Ann'},
{'id': 3, 'name': 'Kim'},
{'id': 4, 'name': 'Olivia'},
{'id': 5, 'name': 'Victoria'}]
df.to_dict('index')
{0: {'id': 1, 'name': 'Emma'},
1: {'id': 2, 'name': 'Ann'},
2: {'id': 3, 'name': 'Kim'},
3: {'id': 4, 'name': 'Olivia'},
4: {'id': 5, 'name': 'Victoria'}}
2. Convert MySQL Table to Pandas DataFrame with mysql.connector
2.1. Install mysql-connector
To start lets install the latest version of mysql-connector - more info - MySQL driver written in Python by:
pip install mysql-connector
2.2. Connect to MySQL database with mysql.connector
The connection to MySQL database requires several properties to be set:
host- the host IP, usually localhost or 127.0.0.1user- the user which will be connected to the MySQLpassword- the password in plain textdatabase- which database will be used
The code below shows the connection to MySQL database - test with user root without password:
import pandas as pd
import mysql.connector
db = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
password="",
database="test"
)
2.3. Read MySQL table by SQL query into DataFrame
Now we can query data from a table and load this data into DataFrame. All we need to do is to create a cursor and define SQL query and execute it by:
cur = db.cursor()
sql_query = "SELECT * FROM girls"
cur.execute(sql_query)
Once data is fetched it can be loaded into DataFrame or consumed:
df_sql_data = pd.DataFrame(cur.fetchall())
Note: If you have problems with encoding or data is shown as bytearray(b'Kim'), you can try to use instead of package mysql-connector with mysql-connector-python:
pip install mysql-connector-python
2.5. Convert MySQL table to Python dictionary full code
import pandas as pd
import mysql.connector
db = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
password="",
database="test"
)
cur = db.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM girls")
df_sql_data = pd.DataFrame(cur.fetchall())
db.close()
df_sql_data.to_dict()
3. Connect to MySQL DataBase with PyODBC
3.1. Install PyODBC on Ubuntu
The installation guide for PyODBC is available here: pyodbc - Installing on Linux.
In short in Ubuntu you need to install dependencies unixodbc-dev by writing in terminal:
sudo apt install unixodbc-dev
If this is not install you will get error during installation of the PyODBC:
fatal error: sql.h: No such file or directory
Next step is to install the Python library in your virtual environment or Python by:
pip install pyodbc
3.2. Install MySQL ODBC driver
Depending on your system you might have drivers installed or not. You can check do you have drivers by:
pyodbc.drivers()
If you get an empty list then you need to install Driver. For MySQL and Ubuntu 18 you can find the instructions here:
Install mysql odbc drivers in ubuntu 18.04: Install mysql odbc drivers in ubuntu 18.04
3.3. Convert MySQL table to Pandas DataFrame with PyODBC
The final step is to** connect to MySQL database by using code** like the one below:
import pandas as pd
import pyodbc
cnn = pyodbc.connect("DRIVER={MySQL};SERVER=localhost;PORT=3306;DATABASE=test;UID=root;PWD=test;CHARSET=utf8;")
sql = 'select * from table'
data = pd.read_sql(sql, cnn)
There are two main points here. The first one is building the connection string - cnn where:
- DRIVER - is the driver installed in the previous section
- SERVER and PORT - address of the database and the port
- UID - is the user
- PWD is the password









