In this post, we'll see how to list files and directory tree structure in Python. We will use Python library and custom code:
(1) seedir - Python library for reading folder tree diagrams
import seedir as sd
path = '/home/user/'
sd.seedir(path=path, style='lines', exclude_folders='.git')
(2) list files and directory trees
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(start_path):
level = root.replace(start_path, '').count(os.sep)
indent = ' ' * 4 * (level)
print('{}{}/'.format(indent, os.path.basename(root)))
list files/folders with seedir
If you want quick and easy solution you can install library: seedir by:
pip install seeder
Then you can use it simply by few Python lines:
import seedir as sd
path = '/home/user/'
sd.seedir(path=path, style='lines', itemlimit=10, depthlimit=2, exclude_folders='.git')
This will return well structured file tree like:
seedir/
├─.gitattributes
├─.gitignore
├─.ipynb_checkpoints/
│ └─examples-checkpoint.ipynb
├─build/
│ ├─bdist.win-amd64/
│ └─lib/
├─CHANGELOG.md
├─dist/
│ └─seedir-0.1.4-py3-none-any.whl
├─docs/
│ ├─exampledir/
│ ├─gettingstarted.md
│ ├─seedir/
│ └─templates/
├─img/
│ ├─pun.jpg
│ ├─seedir_diagram.png
│ └─seedir_diagram.pptx
├─LICENSE
└─MANIFEST.in
There are many different parameters that we can control like:
style='dash'sort=Truefirst='files'depthlimit=2itemlimit=1exclude_folders='.git'
To read more about the API you can visit the official docs: Package seedir.
The method documentation is located here: seedir.realdir.seedir
Directory tree with icons
You need to install Python package emoji in order to visualize the folder and file icons. This can be done by:
pip install emoji
Now we can visualize them by:
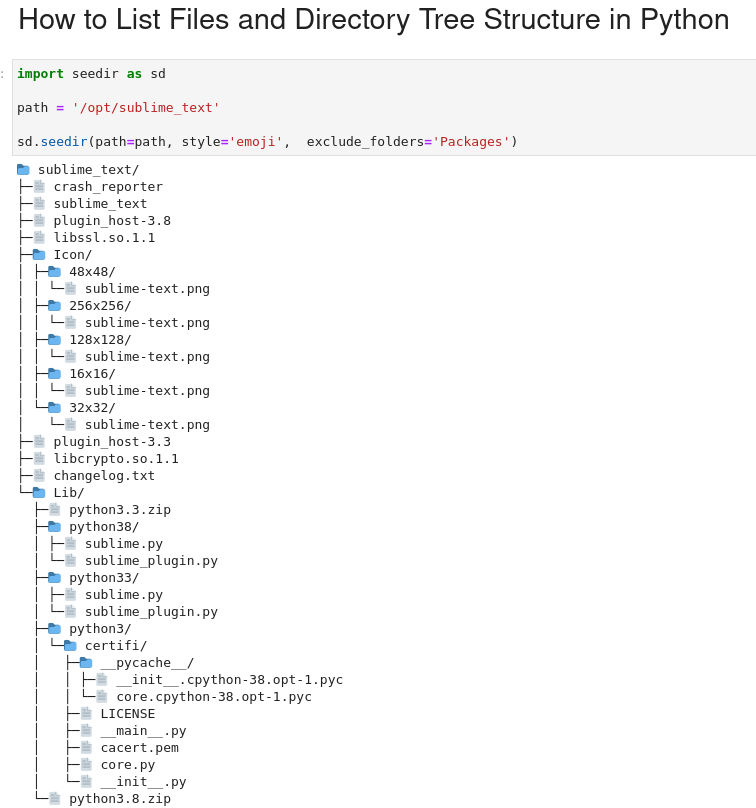
import seedir as sd
path = '/opt/sublime_text'
sd.seedir(path=path, style='emoji', exclude_folders='Packages')
The result is shown on the image below:
Custom solution - list folders and files
If you like to store the result into CSV file or JSON output then you may want to build a custom solution.
Below you can find an example how to list files and folders tree structure with Python code:
import os
def list_files_folders(start_path):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(start_path):
level = root.replace(start_path, '').count(os.sep)
indent = ' ' * 4 * (level)
print(f'{indent}{os.path.basename(root)}/')
subindent = ' ' * 4 * (level + 1)
for f in files:
print(f'{subindent}{f}')
path = '/home/user/'
list_files_folders(path)
The result will be something like:
user/
note1.md
Documentation/
note2.md
note3.md
We will modify the code above in order to store the file structure to Pandas DataFrame in the next section.
Store file/folder tree as DataFrame
If you like to store the file tree with:
- item
- parent
- level
to a Pandas DataFrame we will modify the code to store all the folders as parent and child tree:
import os
import pandas as pd
data = []
def build_tree(root, level):
folder = os.path.basename(root)
parent = os.path.dirname(root)
parent_folder = parent.split('/')[-1]
# print(level, folder, parent_folder)
return [level, folder, parent_folder]
def list_folders(start_path):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(start_path):
level = root.replace(start_path, '').count(os.sep)
indent = ' ' * 4 * (level)
subindent = ' ' * 4 * (level + 1)
data.append(build_tree(root, level))
list_folders('/home/user/')
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.columns = ['level', 'name', 'parent']
df
This will give us:
| level | name | parent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Notes | |
| 1 | 0 | .obsidian | Notes |
| 2 | 1 | themes | .obsidian |
| 3 | 2 | Wombat | themes |
| 4 | 2 | Things | themes |
Now we can easily convert the file and directory tree to JSON or CSV by:
df.to_csv()
df.to_json()
More about those methods can be read here: How to Export DataFrame to JSON with Pandas
Conclusion
In this article, we tried to answer on the following questions:
- How do I get a list of files in a directory tree in Python?
- How do I get a list of files in Python?
- How to get a list of all files in a folder and subfolders in Python?
- How do I get a directory tree in Python?
- Convert directory tree to json in Python









