Simple connection with terminal
mysql -u {username} -p{password} -h {remote server ip} {DB name}
mysql -u root -h XX.XX.XX.XX -p'pass'
mysql -u root -h XX.XX.XX.XX -P 3306 -p password
SSH tunnel via Terminal
ssh -f [email protected] -L 3306:XX.XX.XX.XX:3306 -N
- OSuser - the user of the Ubuntu that has right to connect remotely
- XX.XX.XX.XX: the IP address of the remote server
- -L 3306:XX.XX.XX.XX:3306 binds the local port 3306 to the remote port 3306 on host XX.XX.XX.XX.
Connecting Remotely with HeidiSQL
- install HeidiSQL
- Start HeidiSQL.
- Click New - in Session Manager window.
- Enter a name and press ENTER
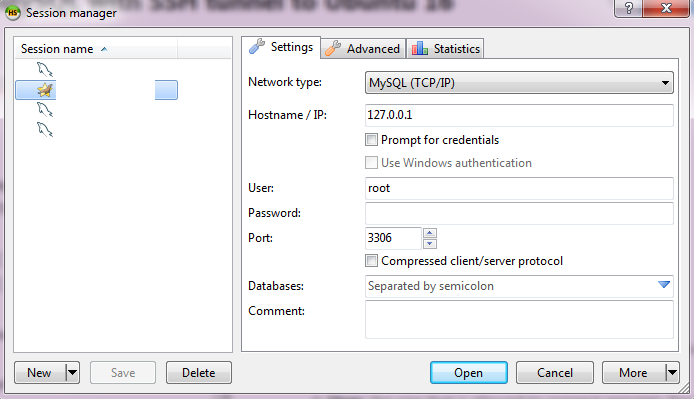
- tab Settings
- Chose network type: MySQL( SSH tunnel )
- Hostname / IP: 127.0.0.1 ( Or a domain name or your server IP address)
- User: the one that is allowed to connect remotely
Password: the password for the database user. - Port: 3306 (or the one that is set up)
- Databases: it's optional or you can put the schema that you need.
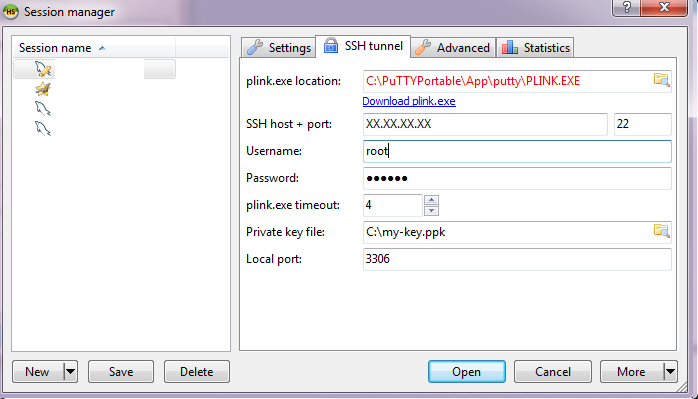
- tab SSH Tunnel
- plink.exe location - the path to plink.exe(which is part of PuTTy). in order to create an SSH tunnel it's needed PuTTY: a free SSH and Telnet client; You can installed it or use it as portable version.
- SSH Host + port: give the address of the server - the one of the database and the port as well: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX : 22
- Username - the OS user used to connect to the server
- Password - the password of the user
- Private key file - in order to connect you need to have private key (example my-key-pass.ppk). You can generate a pair from Ubuntu and Putty.
- The connection should be visible in left window: session names
- Press Open to connect
Connecting Remotely with DBeaver
- Install DBeaver
- New connection
- General
- Enter Port - 22
- Database - test - optional
- User - root - the DB user
- Password - the DB password
- Click Next
- Network
- SSH Tunnel tab
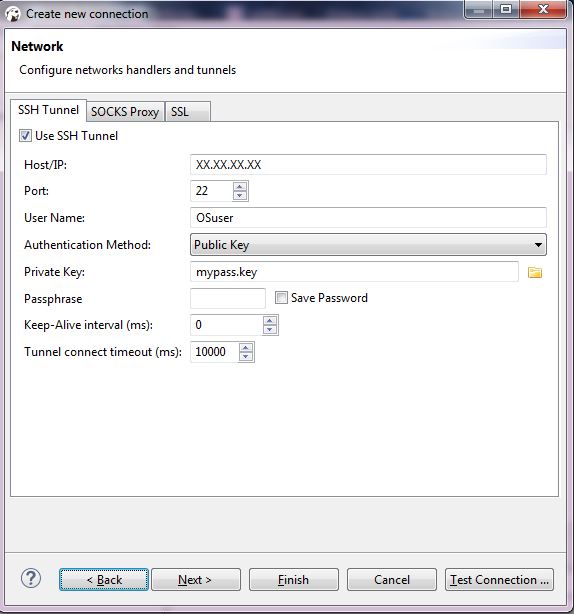
- check Use SSH Tunnel
- Host - the address of the server
- Port - the port
- User Name- the OS user used for connection
- Authentication method - choose Public key ( you can use direct connection if your server is not secured by public key)
- Private Key - path to your key - example mypass.pkk
- Passphrase - if the key is secured by pass
phrase - Click Next
- Final connection settings
- Put Name of the connection
- Test connection
MySQL workbench remote connection
- Install MySQL Workbench
- Open Setup New Connection.
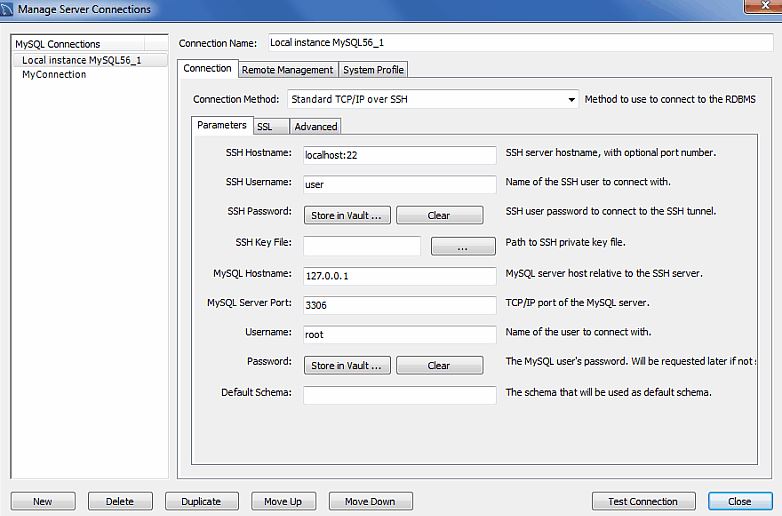
- Enter Connection Name
- Tab Parameters
- Choose Connection Method - Standard TCP/IP over SSH
- SSH Hostname - XX.XX.XX.XX
- SSH Username - The OS user name of the server that you connect to
- SSH Password - the user password
- MySQL Hostname - 127.0.0.1 - db address on the server
- MySQL Server Port - 3306 - the port of the MySQL DB
- Username - root - DB user with right to connect remotely
- Password - the password of the DB user
- Tab SSL
- setup your private key - mypass.ppk
- Information about the setup is available on this page: 5.3.4 SSL Wizard (Certificates)