This is a quick tutorial how to install Jupyter Notebook on Ubuntu 18 or Linux Mint 18.
In this post:
- Prerequisite for Jupyter Notebook/IPython
- Install and run Jupyter Notebook / IPython
- Testing and running simple Notebook
- How to stop or check status of Jupyter
- References
Prerequisite for Jupyter Notebook/IPython
First of all you need to update your cache:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
By default you will have installed python and pip. In order to verify their existence and versions:
python --version
pip --version
in case of missing python and/or pip you can install them by:
sudo apt-get -y install python2.7 python-pip python-dev
or for Python 3
sudo apt-get -y install python3.5 python-pip python-dev
I prefer to install Jupyter in virtual environment so you can create one if you don't have byReferences:
virtualenv --system-site-packages -p python3 jupyenv
then go in the newly created environment and activate it by:
cd jupyenv
source ./bin/activate
you should see terminal change like:
(jupyenv) user@user ~/envs/jupyenv $
in order to stop virtual environment type:
deactivate
returning your terminal to normal.
You can see more about virtual environments here: Install python 3.7 on Linux Mint
Install and run Jupyter Notebook / IPython
After ensuring Python, pip and virtual environment you can install IPython by:
sudo apt-get -y install ipython ipython-notebook
Activate your virtual environment and install Jupyter Notebook in this environment by:
pip install jupyter
if you have errors you can try to upgrade pip by:
pip install --upgrade pip
Now you can run it by:
jupyter notebook
If you like you can create starting script for Jupyter Notebook by:
#!/bin/bash
cd /home/user/envs/jupyenv
source /home/user/envs/jupyenv/bin/activate
jupyter notebook
This will start Jupyter which will be available in the browser by opening address:
http://localhost:8888/tree
Testing and running simple Notebook
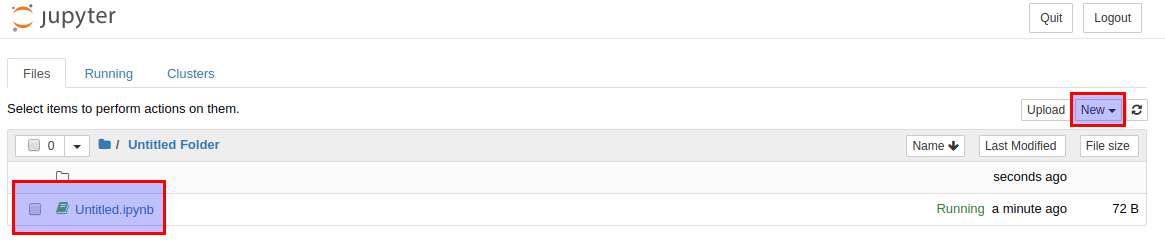
Inside the Jupyter you can create new Notebook from button New and selecting Python 2 or Python 3. Then you can enter python code and run the cell:
for i in range(1, 10, 2):
print(i)
and check the output.
There are many options:
- You can use different Kernel
- Python 2
- Python 3
- Cell Type
- Code
- Markdown
You can create cells with markdown like:
# Notebook Jupyter Notebook
This is a simple example showing for loop and range:
```python
for i in range(1, 10, 2):
print(i)```
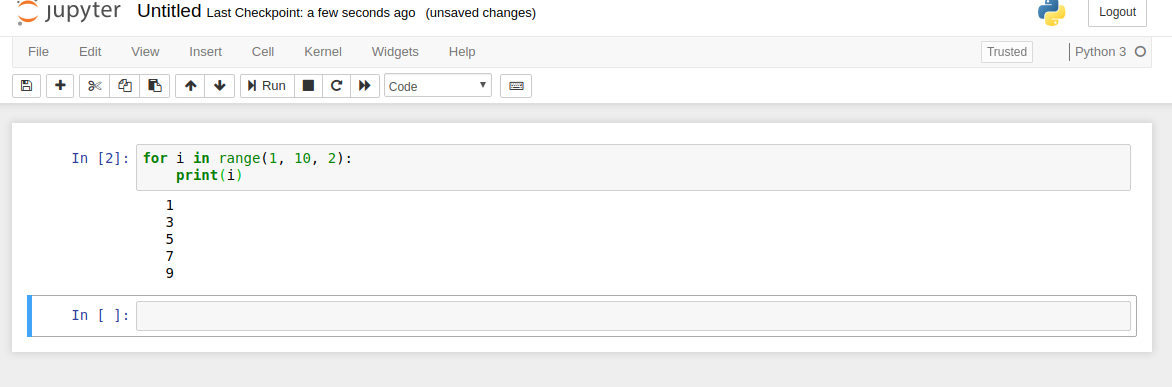
You can create many cells and run them all. In case of problems you can restart the Kernel.
Once you finish with your tests then you can stop the Jupyter by CTRL + C. Your files will be persistent between the restarts.
How to stop or check status of Jupyter
In order to stop Jupyter you can use this command:
jupyter notebook stop 8888
You can check for all running instances by this code:
jupyter notebook list
expected result:
Currently running servers:
http://localhost:8892/?token=b54426bbd5c0a0912137a33aabd775d0ec8e :: /home/user/jupy
http://localhost:8891/?token=baf9fb694459600724dbe1205feda976ebd0 :: /home/user/jupy
http://localhost:8890/?token=1fb8cff5ecc1ea1ac3227bff67242d2331bf :: /home/user/jupy
http://localhost:8889/?token=6e2a519b5488f74ebe82fc6c296d338d2fcc :: /home/user/jupy
http://localhost:8888/?token=866a73699fdf74505f4e5b0bdc0832e5d8a5 :: /home/user/jupy
References
You can do much more with IPython than simply running Python code and discplay Markdown. You can run shell commands, set environmental variables and more. You can check some of the tricks on the links below:









