In this short tutorial, you'll see how to detect borken links with Python. Two examples will be shown - one using BeautifulSoup and the other one will use Selenium.
If you need to check page redirects and broken URL-s from list of pages you can check this article: Python Script to Check for Broken Links And Redirects.
Find Broken Links with BeautifulSoup
The first example is extracting all links on a given URL
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def get_broken_links(url):
def _validate_url(url):
r = requests.head(url)
# print(url, r.status_code)
if r.status_code == 404:
broken_links.append(url)
data = requests.get(url).text
soup = BeautifulSoup(data, features="html.parser")
links = [link.get("href") for link in soup.find_all("a")]
broken_links = []
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=8) as executor:
executor.map(_validate_url, links)
return broken_links
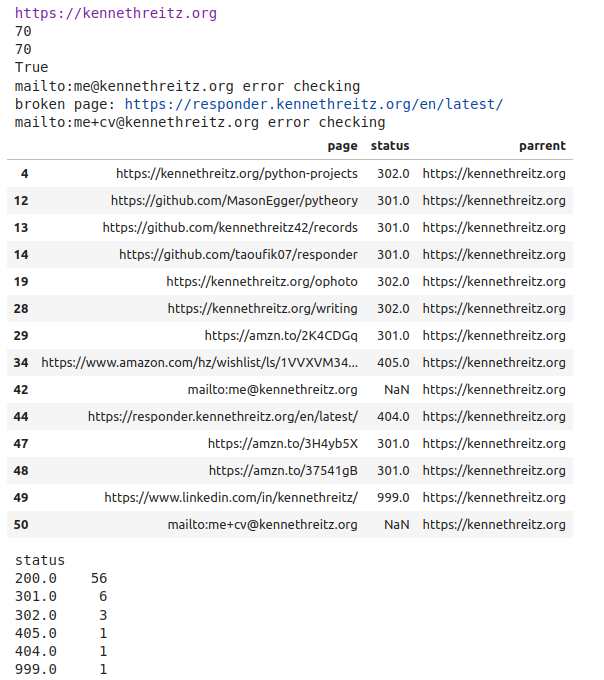
We are checking the website of the creator of the request library: Kenneth Reitz.
The checks show one broken link on his page:
['https://responder.kennethreitz.org/en/latest/']
We can also list each link found and the status code like:
https://pep8.org/ 200
https://github.com/MasonEgger/pytheory 301
https://github.com/kennethreitz42/records 301
https://github.com/jazzband/tablib 200
https://github.com/realpython/python-guide 200
...
https://httpbin.org 200
https://responder.kennethreitz.org/en/latest/ 404
https://github.com/pypa/pipenv 200
...
The code works as follows:
- Defines an inner function
_validate_url(url)to check the validity of each URL by HTTP status - 404 - Retrieves the webpage content using
requests.get(url).text. - Parses the HTML content using BeautifulSoup to extract all links (
<a>tags). - Initializes an empty list broken_links to store broken links.
- Utilizes a ThreadPoolExecutor to concurrently execute _validate_url function for each link with a maximum of 8 workers.
- Returns the list of broken links found during the validation process.
Find broken links with Selenium
First you need to install the https://pypi.org/project/selenium/ package by:
pip install selenium
Then we can use the following code to check multiple pages. The will load the pages in a real browser.
It will check the links in two ways:
- XPATH -
value="//a[@href]" - tag name
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import pandas as pd
from seleniumwire import webdriver
import requests
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
dfs = []
def validate_url(url):
broken_links = []
try:
r = requests.head(url)
if r.status_code == 404:
broken_links.append(url)
print('broken page:', url)
return {'page': url, 'status':r.status_code, 'parrent': page}
except:
print(url, 'error checking')
return {'page': url, 'status':None, 'parrent': page}
def validate_page(page):
driver.get(page)
href_links = []
href_links2 = []
elems = driver.find_elements(by=By.XPATH, value="//a[@href]")
elems2 = driver.find_elements(by=By.TAG_NAME, value="a")
for elem in elems:
l = elem.get_attribute("href")
if l not in href_links:
href_links.append(l)
for elem in elems2:
l = elem.get_attribute("href")
if (l not in href_links2) & (l is not None):
href_links2.append(l)
print(len(href_links))
print(len(href_links2))
print(href_links == href_links2)
data = [validate_url(url) for url in href_links]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
dfs.append(df)
display(df[df['status'] != 200])
display(df['status'].value_counts())
pages = ["https://kennethreitz.org", "https://wikipedia.org"]
for page in set(pages):
print(page)
validate_page(page)
Finally it will display and print stats for the statuses and the broken links: